
Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.
As an important part of the car, the axle conveys the force in all directions between the frame and the road surface, directly affecting the safety and reliability of the car. The fastening bolts used on it are the key components of the axle. Zero defects are often required for fastener products supplied by their suppliers. About 48 hours after the completion of the installation of a certain type of passenger car axle, it was found that one of the fastening bolts broke, and the factory requested to analyze the cause of the fracture. The bolt specification is M10×1.25×128, the performance grade is 10.9, the installation torque is 80±10N•m, the material is 42CrMo, the surface is plated with yellow zinc, and after electroplating, it is treated by hydrogenation at 200°C for 4 hours.
Physical and chemical test
1.1 fracture analysis
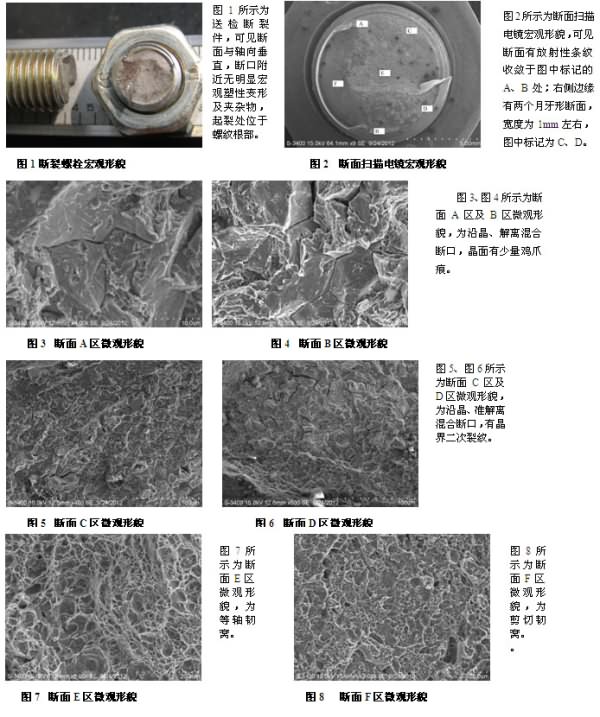

2. Comprehensive analysis
It can be seen from the above analysis that although there is no plastic deformation near the bolt fracture, the microscopic morphology shows that the fracture surface of the fracture surface accounts for about 80% of the total cross-sectional area, indicating that the bolt is subjected to large axial stress when fractured. From the friction coefficient test results, the total coefficient of the bolt friction of the installation manufacturer is 0.11, and the friction coefficient of the thread part is only 0.07, which is obviously less than 0.20 of the manufacturer's inspection bolt. When using torque control installation, a small friction coefficient will cause the bolt to withstand a large axial preload. From the preload force-torque test results, when the installation torque is 80N•m, the installation manufacturer will send the inspection. The bolt pre-tightening force reaches 53.4kN, which is higher than the guaranteed load test stress of the standard specification bolt of 50.8kN, and close to the bolt's yield strength of 57.5kN. When the installation torque is in error, the bolt is likely to be over-screwed.
In addition, the bolt is electroplated, although it is subjected to hydrogen flooding treatment, but the risk of hydrogen residue cannot be completely eliminated [2]. The higher the bolt hardness, the larger the axial preload force and the higher the probability of hydrogen embrittlement. “GB-T 5267.1-2002 Fastener Plating” standard clearly mentions that the hardness of fasteners with a hardness greater than 320HV is hydrogen embrittlement risk. When the hardness is greater than 365HV, the plating treatment is generally not used, and the surface hardness of the broken bolt is used. 365HV has been reached. The hydrogen content test results show that although the hydrogen content of the fracture bolt is below 5μg/g, due to the uneven distribution of hydrogen inside the material, it is easy to accumulate in the stress concentration area at the root of the thread, and the pre-tightening force of the bolt is too large. The action produces hydrogen-induced microcracks at the root of the thread. The tip of the microcrack is the stress concentration zone, and the hydrogen atoms continue to diffuse and accumulate toward the crack tip [3]. When the crack propagates to a certain extent, the bolt loses due to the reduction of the bearing area. Stable fracture.
3. Conclusions and recommendations
Through the above analysis, the following conclusions can be drawn:
First, the fracture property of the bolt is delayed fracture caused by hydrogen, and the excessive pre-tightening force of the installation induces microcracks on the surface, which is the main cause of bolt breakage;
Second, the 10.9 grade bolts are recommended to use Dacromet, powder zinc infiltration and other surface treatment methods to eliminate the risk of hydrogen embrittlement;
Third, the installation manufacturer should strictly control the storage, transportation and assembly of the bolts to prevent oil pollution, and determine the friction coefficient through the axial force-torque test according to the surface condition of each batch of bolts, scientifically and effectively control the pre-tightening force of the bolts. .
Contactar proveedor

Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.

Fill in more information so that we can get in touch with you faster
Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.